Hybrid Mutual Fund : हाइब्रिड म्यूचुअल फंड एक प्रकार का म्यूचुअल फंड है जो निवेशकों को दोनों प्रकार के निवेश, यानी शेयरों (एक्विटीज) और ऋण साधनों (डैट इंस्ट्रूमेंट्स) का मिश्रण प्रदान करता है। इसका उद्देश्य पूंजी की वृद्धि के साथ-साथ स्थिरता भी सुनिश्चित करना होता है।
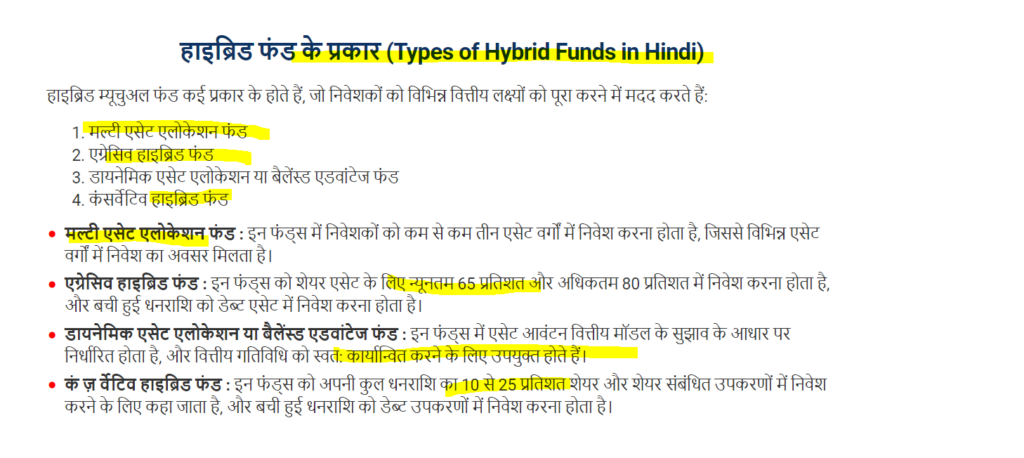
हाइब्रिड म्यूचुअल फंड के मुख्य प्रकारों में निम्नलिखित शामिल हैं:
- आक्रामक हाइब्रिड फंड: इन फंडों में अधिकांश निवेश शेयरों में होता है और कुछ हिस्सा डैट इंस्ट्रूमेंट्स में होता है। इनका उद्देश्य उच्च रिटर्न प्रदान करना होता है, लेकिन इसमें जोखिम भी अधिक होता है।
- संवेदनशील हाइब्रिड फंड: इन फंडों में शेयरों और डैट इंस्ट्रूमेंट्स के बीच संतुलन बनाए रखा जाता है, जिससे जोखिम और रिटर्न का मिश्रण होता है।
- डिफेंसिव हाइब्रिड फंड: इन फंडों में अधिकतर निवेश डैट इंस्ट्रूमेंट्स में होता है और कम हिस्सा शेयरों में होता है। यह विकल्प स्थिर रिटर्न प्रदान करता है और जोखिम कम होता है।
- Hybrid Mutual Fund
इन फंडों का चयन करते समय आपको अपने निवेश के लक्ष्य, जोखिम की सहनशीलता, और समय की अवधि पर विचार करना चाहिए। हाइब्रिड म्यूचुअल फंड एक निवेश पोर्टफोलियो को विविधता देने में मदद कर सकते हैं और विभिन्न बाजार स्थितियों में बेहतर प्रदर्शन करने की संभावना रखते हैं।
1. Asset Allocation Hybrid Mutual Fund
Hybrid mutual funds invest in a mix of equity and debt instruments, with the allocation percentages varying based on the fund’s objective and strategy. For example:
- Aggressive Hybrid Funds: Typically allocate around 65-80% of their assets in equities and the remaining in debt instruments.
- Conservative Hybrid Funds: Might allocate 10-30% in equities and the rest in debt, focusing on lower risk and steady returns.
- Balanced Hybrid Funds: Aim for a balanced approach, with roughly 40-60% in equities and 40-60% in debt.
- SIP
2. Risk and Return Hybrid Mutual Fund
- Equity Portion: The equity component can offer high returns but comes with higher volatility and risk.
- Debt Portion: Provides stability and regular income, reducing overall risk but typically offering lower returns compared to equities.
3. Tax Implications Hybrid Mutual Fund
- Long-Term Capital Gains (LTCG): Gains from equities held for more than one year are subject to LTCG tax.
- Short-Term Capital Gains (STCG): Gains from equities held for less than one year are taxed at a higher rate.
- Debt Instruments: Interest earned from debt instruments is taxed as per the investor’s income tax slab.
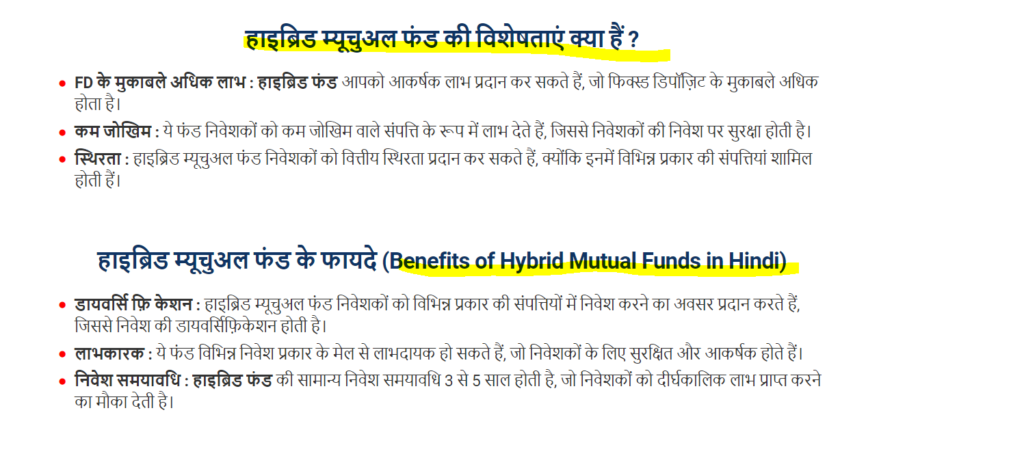
4. Benefits
- Diversification: Provides exposure to both equity and debt, spreading risk across different asset classes.
- Professional Management: Managed by professional fund managers who make investment decisions based on market conditions.
- Suitable for Varying Risk Profiles: Offers options suitable for both conservative and aggressive investors.
5. Drawbacks
- Complexity: Can be more complex compared to purely equity or debt funds.
- Management Fees: May have higher management fees compared to index funds or ETFs due to active management.
6. Suitability
- Investors Seeking Balanced Growth: Ideal for investors who want a mix of growth and stability.
- Risk-Averse Investors: Conservative hybrid funds can be suitable for those who want exposure to equities but prefer to limit their risk.
- Goal-Based Investment: Useful for those with intermediate to long-term financial goals, such as retirement or education funding.
7. Examples
- Balanced Advantage Funds: Adjust their equity-debt mix dynamically based on market conditions.
- Multi-Asset Funds: Invest in multiple asset classes, including equities, bonds, gold, and more.
Choosing the Right Fund
When selecting a hybrid mutual fund, consider factors like:
- Investment Goals: Align the fund’s objective with your financial goals.
- Risk Tolerance: Choose a fund with an appropriate risk profile.
- Expense Ratio: Evaluate the cost of managing the fund.
- Historical Performance: Review past performance, but remember it’s not a guarantee of future results.
By diversifying your investments across different asset classes, hybrid mutual funds can provide a balanced approach to investing, aiming to combine the benefits of equity and debt to meet your financial objectives.
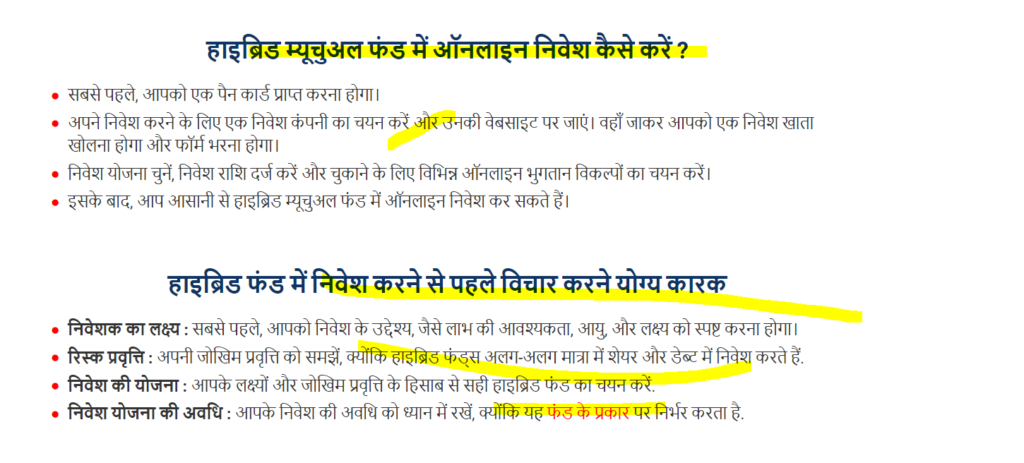
8. How to Invest in Hybrid Mutual Funds : Hybrid Mutual Fund
- Research and Selection: Start by researching various hybrid mutual funds available in the market. Look at their asset allocation, performance history, fund manager experience, and expense ratios. Financial websites, fund fact sheets, and ratings agencies can provide valuable insights.
- KYC (Know Your Customer): Ensure that your KYC process is complete, as it’s a prerequisite for investing in mutual funds. This typically involves submitting identification and address proof.
- Choose an Investment Mode:
- Lump Sum Investment: Invest a one-time amount.
- Systematic Investment Plan (SIP): Invest a fixed amount periodically (monthly or quarterly). SIPs help in rupee cost averaging and disciplined investing.
- Hybrid Mutual Fund
- Submit the Application: Fill out the mutual fund application form, which can usually be done online through the fund house’s website or through mutual fund distributors.
- Monitor and Review: Regularly review the performance of your investments to ensure they align with your goals. Adjust your investments if necessary based on changes in your financial situation or market conditions.
- Hybrid Mutual Fund
9. Key Factors to Consider
- Investment Horizon: Hybrid funds with higher equity exposure are generally suited for a longer investment horizon, while those with more debt can be suitable for shorter-term goals.
- Fund Objectives: Ensure the fund’s investment strategy aligns with your financial goals, whether it’s growth, income, or a balance of both.
- Fund Performance: Analyze historical performance but remember that past performance is not indicative of future results. Look for consistency in returns and how the fund has performed in various market conditions.
- Expense Ratio: Compare the expense ratios of different funds. Lower expense ratios mean more of your investment returns stay with you, although higher fees may be justified if the fund delivers superior performance.
- Tax Implications: Understand the tax impact of investing in hybrid funds, including capital gains and interest income tax implications.
- Exit Strategy: Be aware of the fund’s exit load and redemption terms. Some funds may charge a fee if you redeem your units before a certain period.
- Hybrid Mutual Fund
10. Comparing Hybrid Mutual Funds
When comparing different hybrid mutual funds, consider:
- Equity vs. Debt Allocation: Check the fund’s allocation strategy to determine how it aligns with your risk tolerance and investment goals.
- Fund Manager’s Track Record: Evaluate the experience and track record of the fund manager.
- Historical Performance: Compare the fund’s performance with its benchmark and peers.
- Investment Philosophy: Understand the fund’s investment philosophy and approach.
- Hybrid Mutual Fund
11. Trends and Innovations
- ESG Funds: Some hybrid funds are focusing on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria, catering to socially responsible investors.
- Target Date Funds: These funds automatically adjust the allocation of assets as the target date approaches, usually aligning with retirement or other significant milestones.
- Hybrid Mutual Fund
12. Conclusion
Hybrid mutual funds offer a versatile investment option by blending equity and debt instruments to balance risk and return. They are suitable for investors who seek a combination of growth and stability in their portfolios. By understanding the various types of hybrid funds, their features, and how to invest in them, you can make informed decisions that align with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Regularly reviewing your investments and staying informed about market trends will help you optimize your investment strategy and achieve your financial objectives more effectively.
13. Common Myths about Hybrid Mutual Funds
Understanding and debunking common myths can help you make more informed investment decisions:
- “Hybrid Funds Are Less Risky Than Equities.”
- Reality: Hybrid funds vary widely in their risk profiles depending on their equity-debt allocation. While they do offer diversification, the risk level can still be high if the fund has a significant equity exposure.
- “Hybrid Funds Guarantee Stable Returns.”
- Reality: No mutual fund guarantees returns. Hybrid funds are designed to balance risk and reward, but they are subject to market fluctuations and economic conditions.
- “Hybrid Funds Are Only for Conservative Investors.”
- Reality: Hybrid funds come in various risk profiles. Some are designed for aggressive investors with higher equity exposure, while others cater to more conservative investors with a focus on debt.
- “All Hybrid Funds Have the Same Performance.”
- Reality: Performance varies based on the fund’s management, asset allocation, and market conditions. It’s essential to compare funds based on historical performance and investment strategy.
- “Hybrid Funds Are Too Complicated for Average Investors.”
- Reality: While hybrid funds can be complex, understanding their basic principles—such as their asset allocation and risk-return profile—can help investors make suitable choices.
14. Practical Tips for Investing in Hybrid Mutual Funds
- Diversify Within Hybrid Funds: Don’t put all your money into a single hybrid fund. Diversify across different funds with varying asset allocations to balance risk and return.
- Regular Review: Periodically review the performance of your hybrid funds. Check if the fund’s performance aligns with your financial goals and if the asset allocation still fits your risk tolerance.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of market trends, interest rate changes, and economic indicators that may impact your hybrid fund investments.
- Understand Fund Documents: Thoroughly read the fund’s offer document, including the scheme information document (SID) and key information memorandum (KIM), to understand its investment strategy, risk factors, and fees.
- Consult a Financial Advisor: If you’re unsure about choosing the right hybrid fund or need personalized advice, consider consulting a certified financial advisor. They can help tailor investment strategies to your financial goals and risk appetite.
15. Advanced Considerations
- Fund Flexibility: Some hybrid funds offer flexible asset allocation, allowing the fund manager to adjust the equity-debt mix based on market conditions. This can be advantageous in volatile markets.
- Performance Attribution: Analyze how different asset classes within the hybrid fund contribute to overall performance. This helps in understanding which components are driving returns or contributing to risks.
- Behavioral Biases: Be aware of common behavioral biases, such as overreacting to short-term market movements or focusing too much on past performance. Maintain a long-term perspective.
- Regulatory Changes: Stay informed about regulatory changes that might affect hybrid funds. Regulations around taxation, investment norms, and fund disclosures can impact your investment decisions.
16. Future Outlook
Hybrid mutual funds continue to evolve, with innovations aimed at meeting diverse investor needs:
- Increased Customization: Fund houses are offering more customized hybrid solutions to cater to specific investor preferences and financial goals.
- Technology Integration: Advances in technology are enabling better data analysis and portfolio management, leading to improved fund performance and investor experience.
- Sustainability Trends: There is growing interest in funds that incorporate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria, offering investors the chance to align their investments with their values.
17. Summary : Hybrid Mutual Fund
Hybrid mutual funds offer a balanced approach to investing by combining equity and debt instruments to manage risk and return. They cater to a wide range of investors, from those seeking aggressive growth to those preferring conservative stability. By understanding their features, benefits, and risks, you can make informed investment choices that align with your financial objectives. Regularly reviewing your investments, staying informed about market conditions, and consulting with financial experts when needed will help you make the most of your hybrid fund investments.
18. Case Studies of Hybrid Mutual Funds
To illustrate how hybrid mutual funds work in practice, consider the following hypothetical case studies:
Case Study 1: Aggressive Growth Investor
Investor Profile: An individual in their 30s, seeking long-term capital appreciation and willing to take on higher risk.
Fund Chosen: An aggressive hybrid fund with an equity allocation of 75% and a debt allocation of 25%.
Strategy: The fund aims for high growth by investing primarily in equities, with a smaller portion in debt for stability and income.
Outcome: Over a 10-year period, the fund delivers high returns driven by strong equity market performance. However, it also experiences significant volatility, reflecting the inherent risks associated with high equity exposure.
Investor Action: Regularly monitors the fund’s performance and is prepared for market fluctuations. Adjusts the portfolio periodically to ensure it continues to align with long-term goals.
Case Study 2: Conservative Investor Approaching Retirement
Investor Profile: A person in their late 50s, nearing retirement, seeking stability and income with moderate growth.
Fund Chosen: A conservative hybrid fund with a 30% equity allocation and a 70% debt allocation.
Strategy: The fund focuses on preserving capital and generating steady income while providing some growth potential through a limited equity exposure.
Outcome: The fund provides steady returns with lower volatility compared to more aggressive hybrid funds. It helps the investor preserve capital while providing consistent income as they approach retirement.
Investor Action: Regularly reviews the fund’s performance to ensure it meets income needs and adjusts the asset allocation as retirement nears to further reduce risk.
Case Study 3: Balanced Investor with Medium-Term Goals
Investor Profile: An individual in their 40s with medium-term financial goals, such as funding children’s education.
Fund Chosen: A balanced hybrid fund with a 50% equity allocation and a 50% debt allocation.
Strategy: The fund aims to provide a balance between growth and stability, suitable for medium-term financial goals with a moderate risk appetite.
Outcome: Over a 5-year period, the fund offers a mix of growth and income. It provides relatively stable returns with moderate volatility, suitable for the investor’s time horizon.
Investor Action: Periodically reviews the fund’s performance and rebalances the portfolio if necessary to stay aligned with financial goals.
19. How to Evaluate Hybrid Funds
When evaluating hybrid mutual funds, consider the following criteria:
- Asset Allocation Strategy: Understand how the fund allocates assets between equities and debt. Determine if it aligns with your risk tolerance and investment goals.
- Historical Performance: Compare the fund’s performance against its benchmark and peers. Look for consistency in returns and performance during different market cycles.
- Fund Manager Expertise: Assess the experience and track record of the fund manager. A skilled manager can significantly impact the fund’s performance.
- Expense Ratio and Fees: Review the fund’s expense ratio and any additional fees. Lower expenses can contribute to higher net returns over time.
- Investment Philosophy and Approach: Understand the fund’s investment philosophy and approach to asset allocation. Ensure it matches your investment strategy and goals.
- Risk Metrics: Evaluate risk metrics such as standard deviation, beta, and Sharpe ratio to understand the fund’s volatility and risk-adjusted returns.
- Liquidity and Redemption Terms: Check the liquidity of the fund and any redemption penalties or exit loads. Ensure you can access your funds when needed.
20. Potential Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Over-reliance on Historical Performance: Don’t base your decision solely on past performance. While it provides insight, future performance may vary due to changing market conditions.
- Ignoring Fees: High fees can erode returns over time. Compare expense ratios and consider lower-cost alternatives if appropriate.
- Neglecting Regular Reviews: Failing to review your investment regularly can lead to misalignment with your goals. Periodic reviews help you stay on track and make necessary adjustments.
- Inadequate Diversification: Investing heavily in one type of hybrid fund can limit diversification. Consider diversifying across different funds and asset classes to spread risk.
- Market Timing: Trying to time the market can be risky and often counterproductive. Maintain a long-term perspective and avoid making impulsive investment decisions based on short-term market movements.
21. Final Thoughts
Hybrid mutual funds offer a versatile investment option, combining the growth potential of equities with the stability of debt instruments. By understanding their features, benefits, and risks, and by conducting thorough research, investors can make informed decisions that align with their financial objectives and risk tolerance. Regular monitoring and periodic adjustments to your investment strategy will help ensure that your hybrid fund investments continue to meet your financial goals effectively.
In conclusion, hybrid mutual funds can be a valuable component of a well-diversified investment portfolio, providing a balanced approach to growth and stability. By staying informed and actively managing your investments, you can optimize your financial outcomes and navigate the complexities of the investment landscape with confidence.
22. The Role of Hybrid Mutual Funds in a Diversified Portfolio
Hybrid mutual funds can play a significant role in a diversified investment portfolio, offering several benefits:
- Balancing Risk and Return: By combining equities and debt, hybrid funds offer a way to balance potential returns with risk. This balance can be particularly useful for investors who want growth but also seek some level of stability.
- Diversification: Hybrid funds inherently provide diversification within a single investment vehicle. This can simplify portfolio management by reducing the need to separately manage equity and debt investments.
- Targeting Specific Investment Goals: Hybrid funds can be tailored to meet specific investment goals, such as growth, income, or capital preservation. For example, a hybrid fund with a higher equity allocation may be suitable for long-term growth, while one with a higher debt allocation might be better for income and stability.
- Dynamic Asset Allocation: Some hybrid funds adjust their asset allocation based on market conditions, providing a dynamic approach to managing risk and optimizing returns. This can be beneficial in volatile or changing market environments.
23. Evaluating Fund Performance Metrics
When assessing the performance of hybrid mutual funds, consider the following metrics:
- Total Return: Measures the overall return on the investment, including both income (dividends, interest) and capital gains. Compare the fund’s total return with its benchmark and peers.
- Risk-Adjusted Return: Metrics like the Sharpe Ratio or Sortino Ratio assess returns relative to risk. A higher ratio indicates better returns for a given level of risk.
- Standard Deviation: Indicates the fund’s volatility. A higher standard deviation means greater variability in returns, which reflects higher risk.
- Beta: Measures the fund’s sensitivity to market movements. A beta greater than 1 indicates higher volatility than the market, while a beta less than 1 indicates lower volatility.
- Alpha: Represents the fund’s performance relative to its benchmark, after adjusting for risk. Positive alpha suggests that the fund has outperformed its benchmark.
24. Recent Trends in Hybrid Mutual Funds
- ESG Integration: There is a growing trend toward integrating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors into investment decisions. Hybrid funds incorporating ESG criteria appeal to socially conscious investors.
- Smart Beta and Factor Investing: Some hybrid funds are incorporating smart beta strategies or factor investing, which aim to capture specific risk premia and enhance returns.
- Thematic Investing: Thematic hybrid funds focus on specific themes or sectors, such as technology or healthcare, combining equity and debt investments related to the theme.
- Increased Transparency: Fund managers are increasingly focusing on transparency, providing more detailed information on investment strategies, holdings, and performance metrics.
25. Tax Considerations for Hybrid Mutual Funds
Tax implications can significantly affect the net returns from hybrid mutual funds. Key considerations include:
- Capital Gains Tax: Gains from the sale of fund units are subject to capital gains tax. Long-term capital gains (for investments held over one year) are usually taxed at a lower rate compared to short-term gains.
- Interest Income: Income from debt investments within the hybrid fund is usually taxed as per the investor’s income tax slab.
- Tax Efficiency: Some hybrid funds are designed to be more tax-efficient, potentially by minimizing taxable events or by focusing on tax-advantaged securities.
26. Alternatives to Hybrid Mutual Funds
While hybrid mutual funds are a versatile investment option, investors might consider other alternatives based on their investment goals and risk tolerance:
- Target-Date Funds: These funds automatically adjust their asset allocation as the target date approaches, making them suitable for retirement or other long-term goals.
- Balanced Funds: Similar to hybrid funds but with a fixed asset allocation. These funds maintain a consistent equity-debt mix.
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): ETFs offer exposure to a range of asset classes and can be a cost-effective alternative to hybrid funds. Some ETFs combine equities and bonds in a single fund.
- Individual Stocks and Bonds: For those looking for more control, investing directly in individual stocks and bonds can offer flexibility and customization.
27. Best Practices for Investing in Hybrid Mutual Funds
- Define Your Goals: Clearly define your investment goals and time horizon. Choose a hybrid fund that aligns with these objectives.
- Review Regularly: Regularly review your hybrid fund’s performance and asset allocation to ensure it continues to meet your needs.
- Consider Costs: Be mindful of management fees, expense ratios, and other costs associated with the fund. Lower costs can enhance your overall returns.
- Diversify Within Your Portfolio: Don’t rely solely on hybrid funds. Diversify your investment portfolio across different asset classes to manage risk and optimize returns.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with market trends, economic conditions, and fund updates. Being informed helps you make better investment decisions.
28. Conclusion
Hybrid mutual funds offer a balanced approach to investing by combining the growth potential of equities with the stability of debt instruments. They can be a valuable component of a diversified investment portfolio, catering to a range of risk tolerances and financial goals. By understanding their features, evaluating performance metrics, and considering recent trends, investors can make informed decisions that align with their investment objectives.
Effective management of hybrid mutual funds involves regular reviews, understanding tax implications, and staying informed about market conditions. Whether you are a conservative investor seeking stability or an aggressive investor looking for growth, hybrid mutual funds can provide a versatile and strategic approach to achieving your financial goals.
29. Key Considerations for Long-Term Investors
Long-term investors can benefit significantly from hybrid mutual funds by leveraging their balanced approach to risk and return. Here are some key considerations for maximizing benefits over the long term:
- Compounding Returns: Invest early to take advantage of the power of compounding. Even small, regular investments can grow substantially over time.
- Patience and Discipline: Maintain a long-term perspective and avoid reacting to short-term market fluctuations. Patience and discipline are crucial for achieving long-term investment goals.
- Rebalancing: Periodically rebalance your portfolio to ensure that the asset allocation remains aligned with your investment goals and risk tolerance. This may involve adjusting the mix of hybrid funds and other investments in your portfolio.
- Growth vs. Income: Determine whether you need growth, income, or a balance of both. Hybrid funds with higher equity allocations generally focus on growth, while those with higher debt allocations emphasize income.
- Tax Efficiency: Consider the tax implications of your investments and seek tax-efficient strategies. This might involve holding hybrid funds in tax-advantaged accounts, like retirement accounts, to minimize tax impact.

30. Addressing Common Investor Questions
Q1: How do I choose between aggressive and conservative hybrid funds?
- Answer: Choose based on your risk tolerance, investment horizon, and financial goals. Aggressive hybrid funds are suitable for those seeking higher growth and who can tolerate more risk, while conservative hybrid funds are better for those seeking stability and lower risk.
Q2: What is the impact of market volatility on hybrid funds?
- Answer: Market volatility affects hybrid funds based on their asset allocation. Funds with higher equity exposure may experience greater volatility, while those with higher debt allocation tend to be more stable. Diversification within the fund helps mitigate some of the effects of volatility.
Q3: Can hybrid funds be used for retirement planning?
- Answer: Yes, hybrid funds can be used for retirement planning. They offer a balanced approach, combining growth potential with income and stability. Select funds based on your time horizon and risk tolerance as you approach retirement.
Q4: How do hybrid funds compare with target-date funds?
- Answer: Hybrid funds maintain a relatively fixed or actively managed asset allocation, while target-date funds automatically adjust their asset allocation as the target date (such as retirement) approaches. Both can be suitable for retirement planning, but target-date funds provide a more automated approach.
31. Advanced Strategies with Hybrid Mutual Funds
For experienced investors looking to enhance their portfolios, consider these advanced strategies:
- Tactical Asset Allocation: Adjust the asset allocation based on short-term market conditions or economic forecasts. Tactical adjustments can optimize returns but require a good understanding of market trends.
- Fund of Funds: Invest in hybrid funds that themselves invest in a mix of other mutual funds. This can provide additional diversification and access to different fund managers and strategies.
- Income Enhancement: Use hybrid funds with a higher debt allocation to enhance income in a low-interest-rate environment. These funds can provide stable income through interest payments.
- Sector-Specific Hybrid Funds: Invest in hybrid funds focused on specific sectors or themes, such as technology or healthcare. These funds combine sector-specific equities with debt instruments, offering targeted exposure.
32. The Role of Hybrid Funds in a Changing Economic Environment
Economic conditions can significantly impact the performance of hybrid mutual funds. Here’s how different economic scenarios can influence these funds:
- Rising Interest Rates: Higher interest rates can negatively affect the performance of the debt portion of hybrid funds. Funds with a higher allocation to debt may experience lower returns. Investors may need to adjust their allocations or consider funds with shorter-duration bonds.
- Economic Recession: In a recession, equities may perform poorly, but debt instruments might provide more stability. Hybrid funds with a higher debt allocation can offer better protection during economic downturns.
- Inflation: Inflation can erode the purchasing power of fixed-income investments. Hybrid funds with significant equity exposure may better withstand inflationary pressures compared to those with higher debt allocations.
- Economic Growth: During periods of strong economic growth, equities tend to perform well. Hybrid funds with a higher equity allocation can benefit from increased market returns, while the debt portion provides stability.
33. Evaluating Hybrid Funds in Different Market Conditions
- Bull Markets: In a bull market, hybrid funds with higher equity allocations may outperform those with a more balanced or conservative approach. Look for funds that capture upside potential while maintaining some risk control through their debt investments.
- Bear Markets: In a bear market, hybrid funds with higher debt allocations may provide better protection against market declines. Focus on funds that emphasize capital preservation and income stability.
- Volatile Markets: During periods of high market volatility, hybrid funds with a balanced approach may offer stability by combining equities and debt. Funds with flexible asset allocation strategies can adapt to changing market conditions.
34. Future Outlook for Hybrid Mutual Funds
The future of hybrid mutual funds is likely to be shaped by several trends:
- Increased Customization: Investors will have access to more customized hybrid fund solutions tailored to specific financial goals and risk profiles.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in technology will enhance fund management and data analysis, leading to improved fund performance and investor experiences.
- Sustainable Investing: There will be a growing focus on sustainable and socially responsible investing, with more hybrid funds incorporating ESG criteria.
- Regulatory Changes: Ongoing regulatory changes may impact fund operations and transparency, influencing how hybrid funds are managed and reported.
35. Final Recommendations
- Know Your Needs: Assess your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon before selecting a hybrid mutual fund.
- Diversify Wisely: Use hybrid funds as part of a diversified investment strategy to balance risk and return effectively.
- Monitor and Adjust: Regularly review and adjust your investment strategy based on performance, market conditions, and changes in your personal financial situation.
- Consult Experts: Seek advice from financial advisors if needed to ensure that your investment choices align with your long-term goals.
Hybrid mutual funds offer a flexible and balanced approach to investing, combining the strengths of both equity and debt instruments. By understanding their features, benefits, and risks, and by staying informed about market conditions and trends, you can effectively leverage hybrid funds to achieve your financial objectives and build a well-rounded investment portfolio.

