NEW TELECOM BILL HAS BEEN IMPLEMENTED : Sim Card, Mobile Tariff समेत 1 जुलाई से होने वाले हैं ये 10 बड़े बदलाव| जानिए कौन-कौन से नियम लागु | देश में लागू हुआ नया TELECOM, SIM CARD खरीदने से पहले जान लें नियम !
Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) :NEW TELECOM BILL HAS BEEN IMPLEMENTED
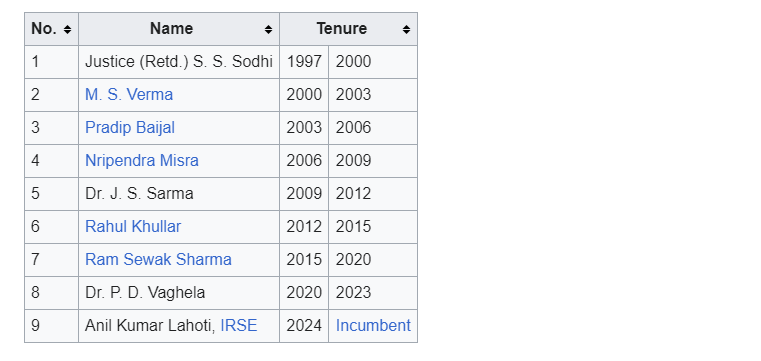
The Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) is the regulatory body responsible for overseeing the telecommunications sector in India. Established in 1997 by the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India Act, it ensures the orderly growth and development of the telecom industry while protecting the interests of consumers and fostering fair competition.
Key responsibilities of TRAI include: NEW TELECOM BILL HAS BEEN IMPLEMENTED
- Regulatory Framework: Formulating regulations, recommendations, and guidelines to govern the telecom sector, including tariffs, quality of service, and licensing norms.
- Consumer Protection: Safeguarding consumer interests by addressing grievances, ensuring transparency, and promoting fair practices among telecom service providers.
- Competition Promotion: Promoting competition and ensuring a level playing field for telecom operators through policies that encourage innovation and investment.
- Spectrum Management: Managing the allocation and efficient utilization of radio frequencies (spectrum) to ensure optimal use and minimize interference.
- Broadband Expansion: Facilitating the growth of broadband services across the country, aiming to enhance digital connectivity and bridge the digital divide.

- Market Research and Analysis: Conducting research, surveys, and studies to analyze market trends, technological advancements, and the impact of policies on the telecom sector.
- Policy Development: Developing and recommending policies to promote the growth and efficiency of the telecom sector, including issues related to infrastructure development, spectrum pricing, and emerging technologies like 5G.
- Interconnection Regulations: Establishing guidelines for interconnection between different telecom networks, ensuring seamless connectivity and interoperability among service providers. NEW TELECOM BILL HAS BEEN IMPLEMENTED
- Quality of Service (QoS): Monitoring and enforcing standards for the quality of telecom services offered by operators, including parameters such as call drop rates, network availability, and customer support.
- Digital Transformation: Initiating measures to facilitate digital transformation across various sectors of the economy through enhanced telecom infrastructure and services.
- International Coordination: Coordinating with international bodies and agencies on matters related to telecom regulation, spectrum harmonization, and global standards.NEW TELECOM BILL HAS BEEN IMPLEMENTED
- Public Consultation: Engaging stakeholders, including telecom operators, consumers, and industry experts, through public consultations and discussions to gather inputs on regulatory matters and policy formulation.
- Telecom Infrastructure Development: Encouraging the deployment of telecom infrastructure, such as towers and fiber optic networks, to improve connectivity and expand coverage across urban and rural areas.
- Consumer Awareness and Education: Promoting awareness among consumers about their rights and responsibilities regarding telecom services, as well as educating them about new technologies and service offerings.
- Regulation of Tariffs: Regulating tariffs charged by telecom service providers to ensure they are reasonable, non-discriminatory, and transparent, thereby protecting consumer interests.

- Enforcement of Regulations: Monitoring compliance with regulatory guidelines and taking enforcement actions against violations by telecom operators to maintain a fair and competitive market environment.
- Data Protection and Privacy: Advising on policies and regulations related to data protection and privacy in the telecom sector, ensuring that consumer data is handled securely and in accordance with legal requirements.
- Dispute Resolution: Resolving disputes and conflicts between telecom operators, consumers, and other stakeholders through mediation, arbitration, or regulatory intervention as necessary. NEW TELECOM BILL HAS BEEN IMPLEMENTED
- Emerging Technologies: Anticipating and responding to technological advancements in the telecom sector, such as Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and blockchain, by formulating relevant regulations and policies.
- Monitoring International Developments: Keeping abreast of global trends and developments in the telecom industry to align India’s regulatory framework with international best practices and standards.
- Promotion of Innovation and Research: Encouraging innovation in telecom technologies and services through policy initiatives, research grants, and collaborations with academia and industry stakeholders. NEW TELECOM BILL HAS BEEN IMPLEMENTED
- Spectrum Auctions and Management: Conducting auctions for spectrum allocation to telecom operators, ensuring efficient utilization of scarce spectrum resources, and formulating policies for spectrum sharing and trading.
- Regulation of Over-the-Top (OTT) Services: Addressing regulatory challenges posed by OTT services (such as messaging apps, VoIP services, and streaming platforms) to maintain a level playing field with traditional telecom services.
- Cybersecurity and Network Resilience: Setting guidelines and standards for cybersecurity measures and ensuring the resilience of telecom networks against cyber threats and disruptions.
- Telecom Market Analysis: Continuously analyzing market dynamics, competition trends, and consumer behavior to inform regulatory decisions and policy reforms aimed at enhancing market efficiency and consumer welfare.
- Collaboration with Government Agencies: Collaborating with other government agencies and departments on issues related to telecom infrastructure, digital governance, and leveraging telecom for socio-economic development initiatives.
- Capacity Building: Conducting workshops, training programs, and seminars for stakeholders to enhance their understanding of regulatory frameworks, compliance requirements, and emerging trends in the telecom sector.
- Regulatory Impact Assessment: Evaluating the impact of regulatory decisions and reforms on stakeholders, industry growth, and broader economic outcomes to ensure effective policy implementation.
- Public Advocacy and Outreach: Engaging with the public, industry associations, and advocacy groups through outreach programs, public consultations, and awareness campaigns to solicit feedback and promote transparency in regulatory processes.
- Future-Proofing Regulatory Frameworks: Anticipating future trends and challenges in the telecom sector, such as the rollout of 5G technology, and proactively adapting regulatory frameworks to facilitate innovation and investment. NEW TELECOM BILL HAS BEEN IMPLEMENTED
- NEW TELECOM BILL HAS BEEN IMPLEMENTED